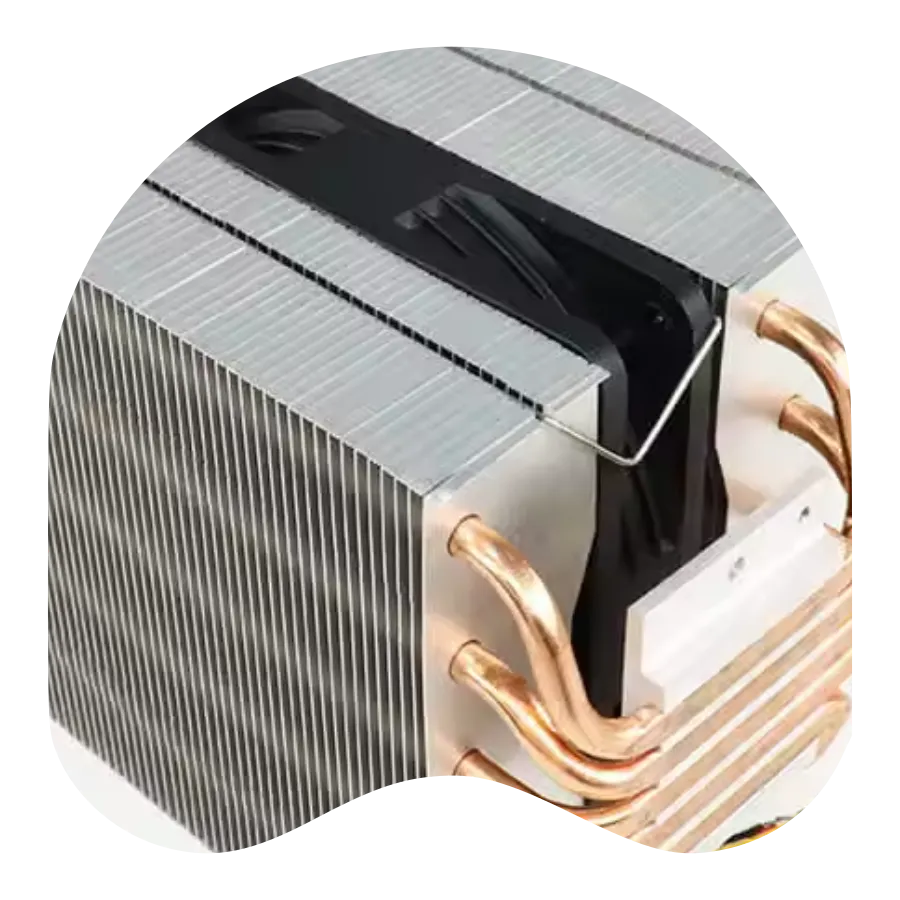
Stacked radiator component manufacturing and processing
Stacked radiator component manufacturing and processing
Stacked radiators are formed by layering specially designed single-tooth fins, multi-tooth fins, or individual profile heat sinks using ultra-high pressure extrusion. This tightly fitted stacked radiator structure allows for dual-plate cooling, with power devices mounted on both sides. This process achieves assembly without any medium, resulting in low development costs, the ability to freely combine radiators of different widths and structures, and strong versatility. It is widely used for heat dissipation in high-power equipment such as power frequency converters and engines. Stacked radiators offer the following advantages: increased heat dissipation area while forming a sealed channel, resulting in better heat dissipation performance; unlimited size; high strength; low production cost; convenient installation and maintenance; and long service life.
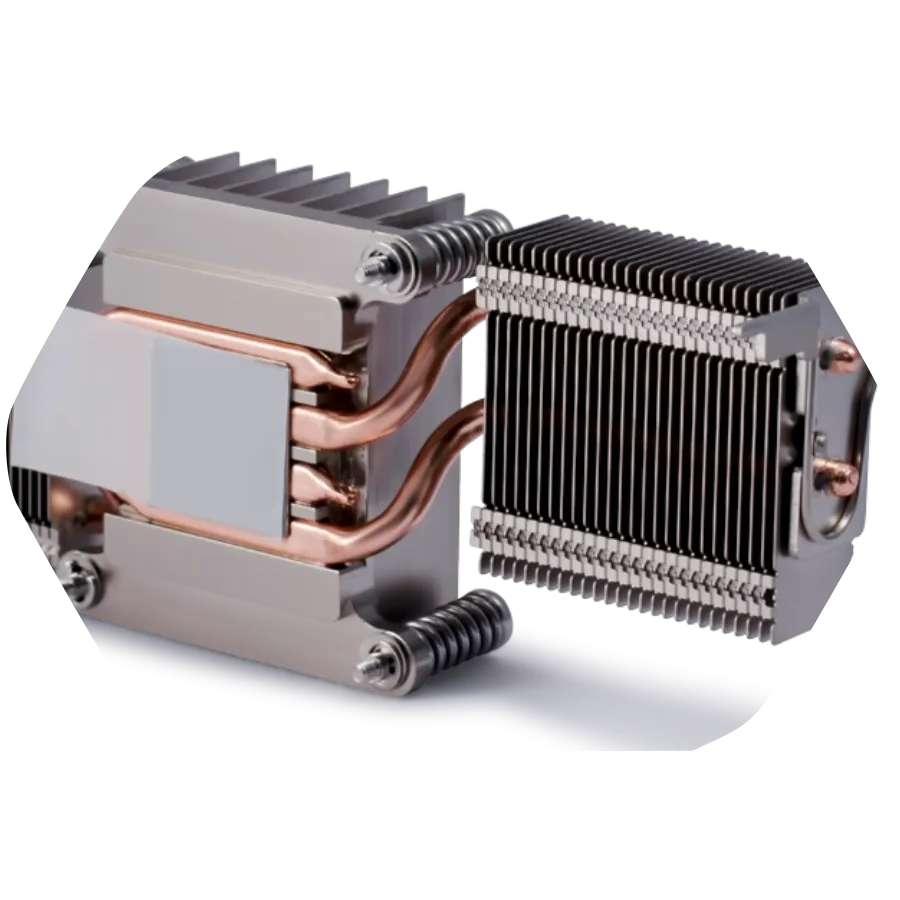

Stacked heat sink application scenarios
Consumer electronics
Smartphones:When components such as the CPU generate heat, the heat can be transferred to the back of the device, the frame, or the screen through thermally conductive materials and heat pipes, and then dissipated through natural convection or a fan.
Laptops: The motherboard, CPU, GPU and other heat-generating components are stacked together, and heat is dissipated through fans and heat sinks to ensure stable performance.
Gaming consoles:Their internal components are densely packed, requiring efficient cooling solutions to handle high loads. This typically involves large heatsinks and multiple fans.
Industrial and Server
Data Centers and Servers: Stacked server racks require good heat dissipation to avoid overheating, typically employing cold aisle or hot aisle designs to dissipate heat through fans and heat sinks.
Industrial controllers: Various electronic components are stacked inside the chassis, and heat is dissipated through heat sinks and fans to ensure stable operation of the equipment in harsh environments.
Transportation
Electric vehicles: The stacking of high-power components such as battery packs and motors requires efficient heat dissipation solutions to prevent overheating and ensure safety and range.
Rail Transit: Electrical equipment in subway, high-speed rail and other vehicles uses stacked heat dissipation, which dissipates heat through fans and radiators.
Other applications
Home appliances:
Built-in steam oven: The heating element, cooling fan and heat sink are stacked and designed with air inlet and outlet, and the heat is dissipated through natural convection or forced air cooling.
Refrigerator:The condenser and heat sink are stacked and installed at the bottom or sides, and the heat is dissipated through the heat sink and fan.
LED Lighting Fixtures: High-power LED lighting fixtures stack heat-generating components on a heat sink and use heat dissipation fins or water cooling to extend the lifespan of the fixture.
Product Features
- High heat dissipation surface area: By stacking a large number of thin fins, a huge heat dissipation surface area can be created within a limited volume, thereby significantly improving heat exchange efficiency.
- High aspect ratio: Stacking technology can achieve a higher aspect ratio (the ratio of fin height to spacing) that is difficult to achieve with traditional extrusion processes, making the fins taller and denser.
- Airflow Optimization: The design of stacked fins can form closed or specific airflow channels (chimney effect), which helps guide airflow to effectively remove heat, especially in active cooling systems that work with fans.
- Material flexibility: Different materials can be selected according to requirements, such as aluminum or copper, or even a hybrid design of copper base and aluminum fins can be adopted to balance thermal conductivity and cost/weight.
- High structural strength: The assembly process, using riveting or fastening, forms a tight and robust overall structure.
